Inositol for PCOS

Inositol is a type of sugar molecule, similar to glucose, but with several substantially different biological functions. Inositol is produced by the body and is found naturally in foods. It has been studied extensively for use as a dietary supplement due to its many potential health benefits for women with PCOS. Fertility specialists worldwide are keenly interested in inositol because research indicates it can help to promote ovulation and pregnancy.
This article will explore the relationship between inositol, PCOS, and insulin to explain why fertility specialists are so excited about this natural, low-intervention, and low-cost treatment. We will also review how inositol may improve ovulation and pregnancy rates, the ideal inositol dosage for PCOS, and the different types of inositol.
Get ready; here comes everything you need to know about inositol and PCOS.
Fast Facts on Inositol and PCOS
- PCOS is the most common cause of infertility worldwide. PCOS is greatly associated with high insulin levels. High insulin levels have been shown to disrupt hormone production, which can cause several PCOS symptoms, including excess body hair, anovulation, and infertility. Many fertility specialists, therefore, theorize that high glucose and insulin levels and the subsequent insulin resistance are the root cause of PCOS.
- Inositol has been demonstrated to improve insulin sensitivity, manage blood glucose levels, and reduce insulin resistance.
- Research has shown that PCOS patients have naturally lower Inositol levels. This deficiency further contributes to several PCOS symptoms.
- Taking Inositol supplements can help promote ovulation and pregnancy in women with PCOS.
- Inositol can also help to improve clinical pregnancy rates in infertile women without PCOS undergoing In-vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) procedures.
- The exact mechanism by which inositol improves ovulation and pregnancy outcomes in those with PCOS is not fully understood but likely linked to glucose and insulin levels, as mentioned above and explained in further detail below.
- Inositol is one of many supplements that may help to improve PCOS symptoms and pregnancy odds.
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal endocrine disorders in women and is the leading cause of infertility, accounting for approximately 20-25% of all cases. It is characterized by several different symptoms, most prominently irregular or absent menstrual cycles and increased testosterone activity. Women with PCOS’ ovaries make an increased amount of testosterone which can cause an imbalance of hormones leading to a laundry list of symptoms, including insulin resistance, anovulation, and infertility.
The exact cause of PCOS remains a mystery. However, research has shown that many women with PCOS have reduced sensitivity to certain functions of insulin. As a result, many PCOS patients have too much insulin in their bodies. Insulin is of course the hormone whose primary job is to promote the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells, but it has many other roles and effects. High insulin levels can cause the ovaries to make more androgen hormones like testosterone. This may explain why testosterone levels are higher in PCOS patients.
What is Inositol?
Inositol is a biological compound that exists in many forms called isomers. Myo-inositol (MYO) and D-chiro-inositol (DCI) are the two main types that are used in fertility supplements. Inositol is used to treat many different medical conditions, including respiratory syndromes, diabetes, PCOS, etc.
Inositol is recommended to treat many conditions because it has many functions and is involved in various bodily processes. It is also involved in several different reproductive processes , affects chemical messengers in the brain, is a major component of cell membranes , and it participates in insulin signaling and glucose metabolism.
Inositol is found naturally in many foods like fruits, nuts, whole grains, and vegetables. In women with PCOS, the mechanism needed to convert inositol into its bio-available inositol is obscured. This causes a decrease in available inositol (as myo-inositol or D-chiro-inositol), which can impact all of the bodily processes mentioned above and cause infertility .
Most fertility supplements contain inositol in its already bioavailable forms like myo-inositol or D-chiro-inositol. Later in this article, we will discuss how to choose the correct fertility supplements to ensure you are getting inositol in its most bioavailable form.
How Inositol Improves PCOS Patients Health and Fertility
As previously mentioned, many women with PCOS have high insulin levels in their bodies due to reduced sensitivity to certain functions of insulin. Women with PCOS are about 30% more likely to be insulin resistant, meaning their bodies can make insulin, but they can’t use it effectively. High insulin levels can cause the ovaries to make excess testosterone leading to hormone imbalances, especially the ratio of luteinizing hormone (LH) to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). High levels of LH further contribute to the high levels of androgens, and low FSH levels impair egg development and ovulation.
Inositol has been shown to play a significant role in insulin signaling and glucose metabolism. Research has shown that supplementing inositol can improve insulin-receptor activity and help to restore insulin resistance in women with PCOS. In fact, it has been demonstrated that myo-inositol may decrease insulin resistance by approximately 70%.
Myo-inositol’s ability to reduce insulin resistance has been shown to cause a decrease in circulating insulin and total testosterone levels. Reduced testosterone levels can help to correct hormonal imbalances that lead to anovulation and decrease pregnancy chances. Researchers have conducted studies to confirm these findings and to show that inositol improves fertility by correcting hormonal imbalances.
In one study, researchers measured the effects of inositol supplementation on hormonal parameters for PCOS patients. After 12 weeks of inositol supplementation, LH, and testosterone levels were reduced significantly, and the ratio of LH to FSH improved. Insulin sensitivity also improved significantly, and menstrual cyclicity was improved for all participants. Researchers concluded that inositol helped to improve reproductive function in PCOS patients by reducing the hyperinsulinemic state that affects LH secretion and causes hormonal imbalances.
Women with PCOS may require proper inositol supplementation because their bodies have difficulty converting inositol into its bioavailable forms like myo and DCI. Due to myo and DCI’s role in insulin signaling and glucose metabolism, their shortage in PCOS patients may further contribute to insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. This increases women with PCOS’s chances of developing type 2 diabetes and other conditions.
Inositol’s Ability to Improve Ovulation for PCOS Patients
To get pregnant, your ovary must release an egg into your fallopian tube. This process is also known as ovulation. Many women with PCOS do not ovulate regularly or at all due to hormonal imbalances. As a consequence of these ovulatory issues, many women with PCOS are unable to achieve pregnancy. Research has shown that inositol supplementation can help to correct these hormonal imbalances to increase ovulatory activity.
In one study, researchers measured the effects of inositol supplementation on 25 infertile women with PCOS. 22 of the women from the study (88%) experienced at least one spontaneous menstrual cycle during treatment. 72% of participants maintained normal ovulatory activity for 6 months. 10 of the participants (40%) developed singleton pregnancies. Researchers concluded that inositol supplementation is capable of restoring spontaneous ovarian activity and consequently fertility in most patients with PCOS.
Inositol’s Ability to Improve Oocyte Quality
Now that the body is ovulating and releasing an egg, it is equally important to ensure the egg or oocyte quality. Oocyte quality has a strong and direct correlation to successful fertilization and clinical pregnancy rates. Research has shown that inositol can help to improve oocyte quality, especially in PCOS women.
In one study, researchers measured the efficacy of inositol to improve oocyte quantity and quality for patients undergoing IVF treatment. At the end of the study, the number of follicles of diameter > 15 mm and the number of oocytes recovered was significantly greater for the inositol treatment group. The average number of embryos transferred and embryo quality were also significantly higher for the inositol group. Researchers concluded that inositol is useful to help PCOS patients undergoing fertility treatment thanks to its insulin-sensitizing activity and its role in oocyte maturation.
Another study aimed to measure if inositol supplementation can improve the oocyte quality, embryo quality, and several other fertility-related factors in PCOS patients undergoing IVF treatments. Participants were split into two groups, an inositol treatment group, and a control group. The ratio of follicles to retrieved oocytes was better for the inositol group. Out of the 233 oocytes collected in the inositol group, 136 were fertilized (58.3 %). Out of the 300 oocytes produced for the control group, only 128 were fertilized (42.6%).
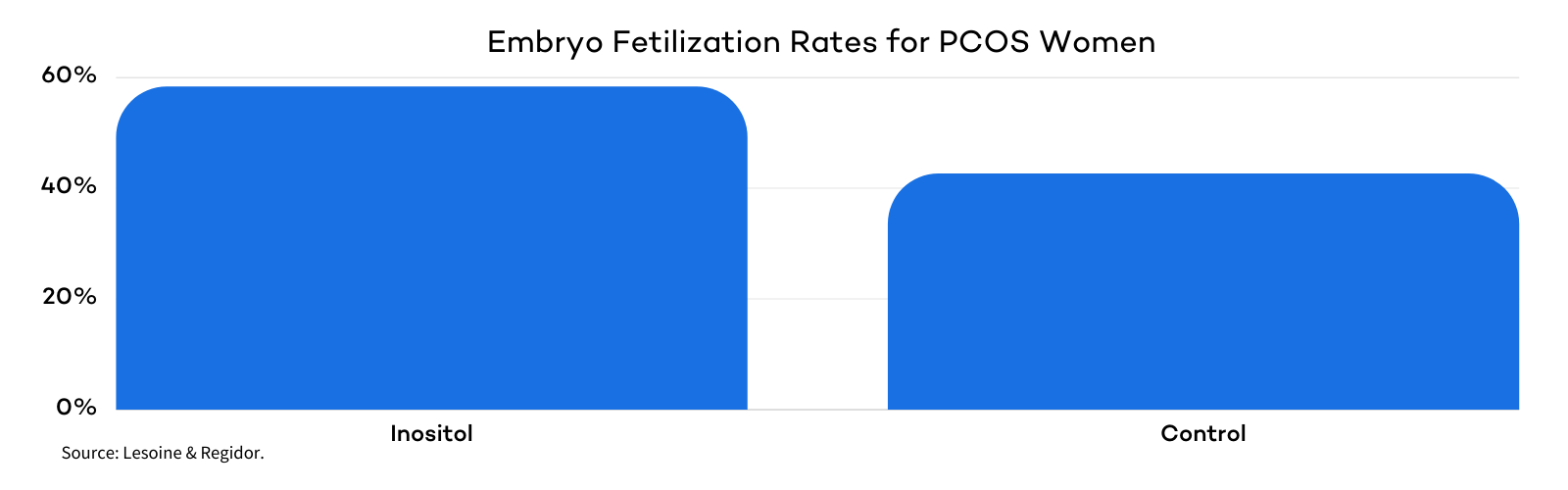
The number of grade I embryos obtained was also higher for the inositol treatment group. Researchers concluded that inositol therapy in women with PCOS results in better fertilization rates and better embryo quality. Due to the smaller number of retrieved oocytes in the inositol group, the risk of hyperstimulation syndrome can also be reduced.
Inositol and Pregnancy Rates for PCOS Patients
Now that we know inositol supplementation has been shown to improve ovulation and egg/embryo quality; you are probably wondering if it can affect pregnancy rates. The answer is yes, inositol has been demonstrated to improve pregnancy rates in some studies!
In one study, researchers measured the effects of inositol supplementation on 116 infertile women with PCOS. After three months of inositol therapy, researchers saw a significant improvement in participant’s metabolic and hormonal parameters. After six months, the clinical pregnancy rate of the inositol treatment group was 45.5%. Researchers concluded that inositol can be used as an insulin sensitizer to improve metabolic, hormonal, and reproductive outcomes in infertile PCOS women.
Other studies have produced similar results in support of inositol supplementation to improve pregnancy rates. In seven trials with 935 participants, inositol supplementation was associated with significantly improved clinical pregnancy rates.
Inositol Dosage for PCOS
Inositol supplementation is known to have very few side effects. However, the ratio of myo to DCI taken and their respective dosages have been shown to have a significant impact on oocyte quality and ovarian response.
Myo-inositol is naturally the most abundantly found form of inositol in our bodies. At high concentrations, it has been shown to ensure healthy oocyte maturation in the ovary. When used in conjunction with IVF protocols, myo-inositol supplementation has been shown to improve oocyte quality and reduce the number of fertility medications needed for ovarian stimulation.
On the other hand, high concentrations of DCI have been shown to affect fertility negatively. In one study, researchers treated PCOS women with high levels of DCI. DCI supplementation at high levels caused a significant decrease in the number of mature embryos and an increase in the number of immature embryos when compared to the control group. The higher the DCI dose (and the more imbalanced the myo to DCI ratio was), the worse the oocyte quality and ovarian response became. Taking too much DCI worsens oocyte quality and ovarian response.
DCI is mainly included in fertility supplements to help maintain the body’s ideal physiological ratio. A ratio of 40:1 myo to DCI is optimal for most tissues in the human body. To ensure optimal results, look for supplements with that same ratio of myo to DCI.
In Conclusion
Supplementing inositol can have many health benefits for women with PCOS. When taken at the right dosage and ratio, inositol can alleviate various PCOS symptoms and boost the fertility of any woman trying to get pregnant. It can increase clinical pregnancy rates in infertile women and improve the quality of embryos.
As with all supplements, be sure to do your research and look for products that contain high-quality and bioavailable ingredients in the appropriate dosage.





