Getting Pregnant With PCOS

Getting pregnant with PCOS can be difficult, which makes sense because it is the leading cause of infertility. Since PCOS is so common, it is well researched and there are many natural solutions and medical treatments available. Of course, other factors significantly impact women with PCOS’s chances of getting pregnant like age. Getting pregnant at 30 is easier than getting pregnant with PCOS at the age of 40.
In this article, we are going to provide a quick overview of what PCOS is, discuss ways to improve PCOS symptoms, and treatment options that can help you get pregnant with PCOS.
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common endocrine disorders that affect women of reproductive age. The most common sign of PCOS is irregular, infrequent, or non-existent periods. Women with PCOS may experience less than eight periods in a year. Irregular periods can be caused by cysts on the ovaries, another common symptom of PCOS. These cysts are small fluid-filled sacs that produce excess levels of male sex hormones called androgens. When women produce abnormally high levels of androgens, it is a medical condition called hyperandrogenism. Hyperandrogenism can prevent women from ovulating. It can also cause additional symptoms found in PCOS patients like oily skin, acne, and male pattern baldness.
PCOS symptoms are not universal, and the signs and symptoms vary from woman to woman.
Common Signs and Symptoms of PCOS include:
- Irregular periods
- Access androgens
- Polycystic ovaries
- Anovulation
- Infertility
- Obesity
- Insulin resistance
- Access body hair
- Oily skin or acne
- Thinning hair or baldness
The exact cause of PCOS is difficult to pinpoint because all of the symptoms influence and affect one another. Fertility specialists believe that PCOS may be the result of a combination of factors including genetics, health, and lifestyle . Many women are completely unaware they have PCOS until they struggle to get pregnant and seek the assistance of a fertility specialist.
Odds of Getting Pregnant with PCOS Naturally
Simply put, PCOS can prevent ovulation, the release of an egg. Without ovulation, pregnancy cannot occur during that cycle. A diagnosis of PCOS does not mean you can’t get pregnant either naturally, or with assisted reproductive treatments, but it can make the journey longer and more difficult. Because the symptoms of PCOS and their severity are so variable, there is no specific statistic we can highlight to provide odds or a percent chance of getting pregnant.
In one cross-sectional study of the Australian Longitudinal Study on Women’s Health (ALSWH), researchers found that 72% of women with PCOS reported infertility. 16% of women from the study without PCOS reported infertility. In this study, women with PCOS were 4.5 times more likely to report infertility. Infertility reporting was significantly higher in women with PCOS .
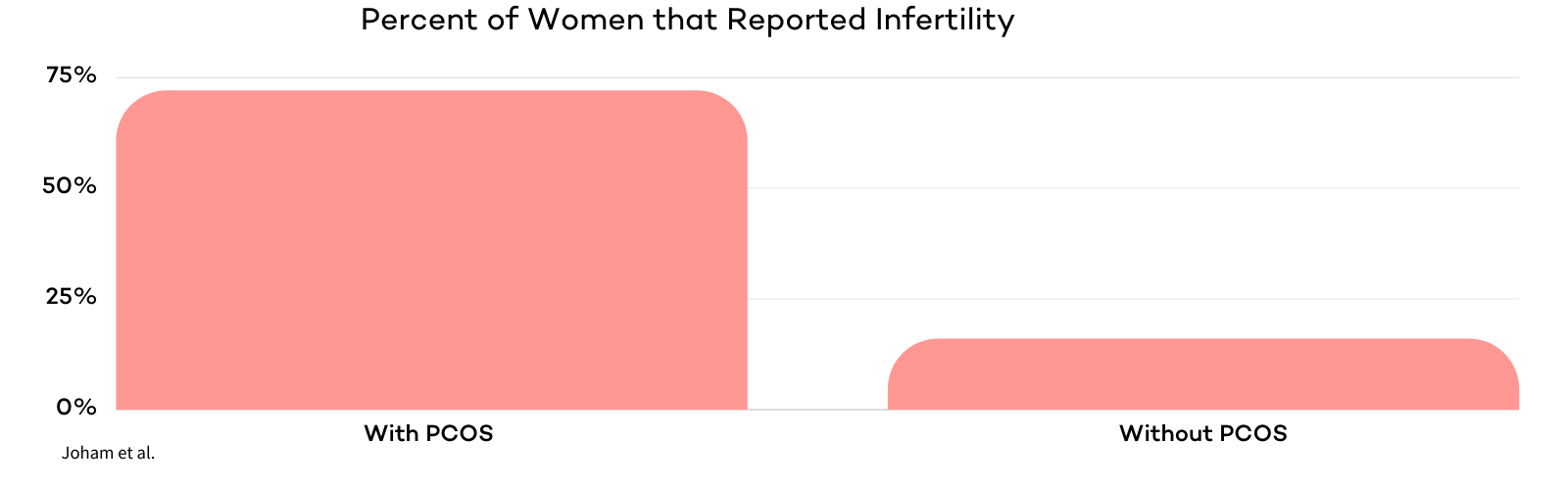
Why do those with PCOS have trouble getting pregnant?
Women with PCOS have higher than normal antral follicle counts (20 to 30+) on either one or both of their ovaries. The high levels of androgens and other sex hormones found in women with PCOS interfere with antral follicle growth. Hormonal imbalances can cause follicles to mature improperly and not release an egg. When a woman does not release an egg during a menstrual cycle, it is known as anovulation. Anovulatory infertility is a common consequence of PCOS, and 70-80% of women with anovulatory infertility have PCOS .
Age and Its Effects on Getting Pregnant with PCOS
Women without PCOS who ovulate regularly see a decrease in oocyte count and live birth rate as they age. When these women reach the age of 35-37, their egg count (ovarian reserve) decreases significantly. Since women with PCOS commonly experience ovulation issues and do not release eggs as regularly, they don’t see the same drastic decline in fertility as they age. Research has shown that women with PCOS show sustained fertility with advancing age . In this study, women with PCOS between the ages of 22-41 showed stable;e oocyte counts and live birth rates. In another study, researchers found that PCOS patients undergoing IVF treatment showed better oocyte and embryo quality compared to normally ovulating women without PCOS who were the same age .
How to Naturally Increase Chances of Getting Pregnant with PCOS
PCOS symptoms are typically more severe for those who are overweight or obese. Being overweight can contribute to ovulatory dysfunction. Some overweight women have an ovulatory deficiency that may not be as severe or occur at all if they were a “normal” weight. As such, some women are mistakenly lumped into the PCOS category. For these women, weight loss will improve their chances of getting pregnant naturally. Please note, this is not always the case as PCOS can cause some women to gain weight.
Women with PCOS are often insulin resistant, meaning their bodies can make insulin, but they can’t use it effectively. This increases women with PCOS’s chances of developing type 2 diabetes. In fact, more than 50% of women with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by the age of 40. Women with PCOS who are overweight are also at risk of developing serious health conditions like gestational diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
It is extremely important for women with PCOS to be cognizant of their weight and health prior to, during, and after pregnancy. Making changes to your diet, exercise, and taking supplements can help to naturally mitigate health risks and increase your chances of getting pregnant with PCOS.
Click here for additional information on improving your natural fertility!
Diet
PCOS has been described as a low-level chronic inflammation condition. Inflammation happens to be one of the main causes of infertility for both women with and without PCOS. Chronic inflammation is caused by micro contaminants that enter our bodies through what we eat and drink. Inflammation can cause difficulty in achieving pregnancy, maintaining pregnancy, or recurrent miscarriages. At CNY Fertility, we recommend PCOS patients eat a high fat, moderate protein, and low to no carbohydrate diet, nicknamed the B.E.B.B.I. Diet Bacon, Eggs, Butter, Beef, and Ice cream made from full-fat heavy cream (with little sugar).
As previously mentioned, PCOS patients are at a higher risk of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes. New research suggests that carbohydrates are responsible for the increase in obesity and other chronic conditions related to PCOS. The standard American diet is a carbohydrate-rich diet that causes chronically elevated blood sugar levels. The sugars and carbohydrates we eat directly influence our blood sugar and insulin levels. PCOS patients are already more susceptible to insulin resistance, so it is important to minimize these levels. When insulin or blood sugar levels get too high, reproductive hormone levels can further be thrown off, which can worsen PCOS patient’s chances of anovulation and directly hurt their fertility.
Recently, more research has been focused on the ketogenic diet’s ability to reduce and improve PCOS symptoms because low carbohydrate diets have been shown to reduce insulin resistance. In one small study, researches focused on the effects of a low carbohydrate ketogenic diet on overweight and obese women with PCOS. For the 5 women that completed the study, they saw a 12% reduction in body weight, a 22% percent decrease in free testosterone, and a 54% reduction in fasting insulin compared to their baseline results after 24 weeks . The study concluded that a low carbohydrate ketogenic diet can help to reduce weight, percent free testosterone, LH/FSH ratio, and fasting insulin in women with obesity and PCOS. A 2013 study of 30 women with PCOS produced similar results. Researchers found that even a small reduction in daily carbohydrate intake can cause significant improvements in hormone production, weight, and additional PCOS risk factors .
The ketogenic diet calls for high levels of fat, which makes it great for PCOS patients struggling to get pregnant because fat is the key element of fertility. Fat provides essential building blocks for our cells and helps synthesize vital reproductive hormones. Dietary fat provides our bodies with energy and essential fatty acids that we can’t produce on our own. Combining the ketogenic diet, anti-inflammatory foods, exercise, and additional healthy lifestyle changes can help lower inflammation and ease PCOS signs and symptoms.
Exercise
The benefits of exercise for fertility and overall health are well documented. In addition to helping PCOS patients lose weight, it can help strengthen your heart and improve circulation. Improved circulation caused by exercising pushes more nutrient-rich blood to the reproductive organs. When people think of exercise, they think of lifting weights or running on a treadmill. For most people, that likely doesn’t sound very appealing. When we say exercise, what we recommend is incorporating low-intensity movement into your daily routine. Stretching, walking, and yoga are all great ways to get your body in motion without the requirement of a gym membership or any equipment.
Research has shown that exercise can significantly improve menstrual cycle regularity and ovulation in about 50% of women diagnosed with PCOS . Exercise can help women with PCOS to lose weight and reduce their BMI. Research has shown that losing weight can also help reduce the amplitude of luteinizing hormone (LH) and as a result, reduce androgen production .
Yoga
Yoga is great for PCOS patients because it helps to boost and balance your immune system. Inflammation is the immune system’s response to foreign invaders or injury. Practicing yoga can help to reduce inflammation, which, as mentioned above, affects fertility, especially in PCOS patients. Yoga can also help you to relax and find your inner calm, which in turn can help raise the number of white blood cells in the body. A PCOS diagnosis can certainly be stressful. It is important to manage stress throughout treatment and seek support if needed.
Click here to visit our fertility support page!
Fertility Supplements and Vitamins
Many of the vitamins and nutrients found in fertility supplements can also be obtained by eating different foods. It is nearly impossible to ensure your body is getting all of the vitamins and minerals it needs to reduce PCOS symptoms and support reproduction through food alone.
Fertility supplement popularity continues to rise as new research emerges in support of different vitamins and minerals for overall and reproductive health. Studies have shown that certain supplements can have beneficial effects on PCOS-related symptoms such as immature oocytes, hyperandrogenism, and increased BMI .
Inositol
Inositol is a type of sugar that plays an essential role in many different bodily functions. Inositol is a significant component of cell membranes, it influences insulin production, and it affects chemical messengers in the brain. Poor ovarian response, a symptom of PCOS, is reported in 9-24% of all IVF cases.
Gonadotropin fertility drugs are commonly prescribed to PCOS patients undergoing fertility treatment to increase their ovarian response. Women are considered “poor responders” if their ovaries don’t increase production after taking gonadotropin fertility drugs. Studies have shown that inositol can significantly improve ovarian response in women being treated with gonadotropins . Inositol is especially recommended for “low responders” and PCOS patients undergoing IVF treatment.
Insulin resistance is a key feature of most women with PCOS. Inositol has been shown effective to correct insulin resistance in patients with PCOS. A 2016 study showed that supplementing inositol can help treat insulin resistance, lower body mass index, and improve ovarian activity in PCOS patients .
Carnitine
Acetyl L-Carnitine (ALC) is an antioxidant that is naturally produced by the body. ALC helps the body turn fat into energy. A clinical study found that non-obese women with PCOS have significantly lower levels of L-carnitine when compared to women without PCOS . The researchers who conducted the study believe that low ALC levels could be linked to hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance. A clinical trial in women with PCOS found that supplementing ALC with clomiphene provided a thicker endometrium and higher pregnancy rates . Keep reading below for more information about the use of clomiphene to treat PCOS.
Vitamin D
67 to 85% of women with PCOS suffer from vitamin D deficiency . Low vitamin D levels may intensify the symptoms of PCOS, including insulin resistance, ovulatory, menstrual irregularities, infertility, hyperandrogenism, and obesity. Supplementing vitamin D has been shown to have beneficial effects on menstrual regularity and ovulation .
Research has shown that vitamin D supplementation can also positively impact pregnancy rates and fertility treatment outcomes. In one study, women with adequate levels of vitamin D had a 52.5% chance of achieving pregnancy per IVF cycle compared to a 34.7% chance for women with inadequate levels .
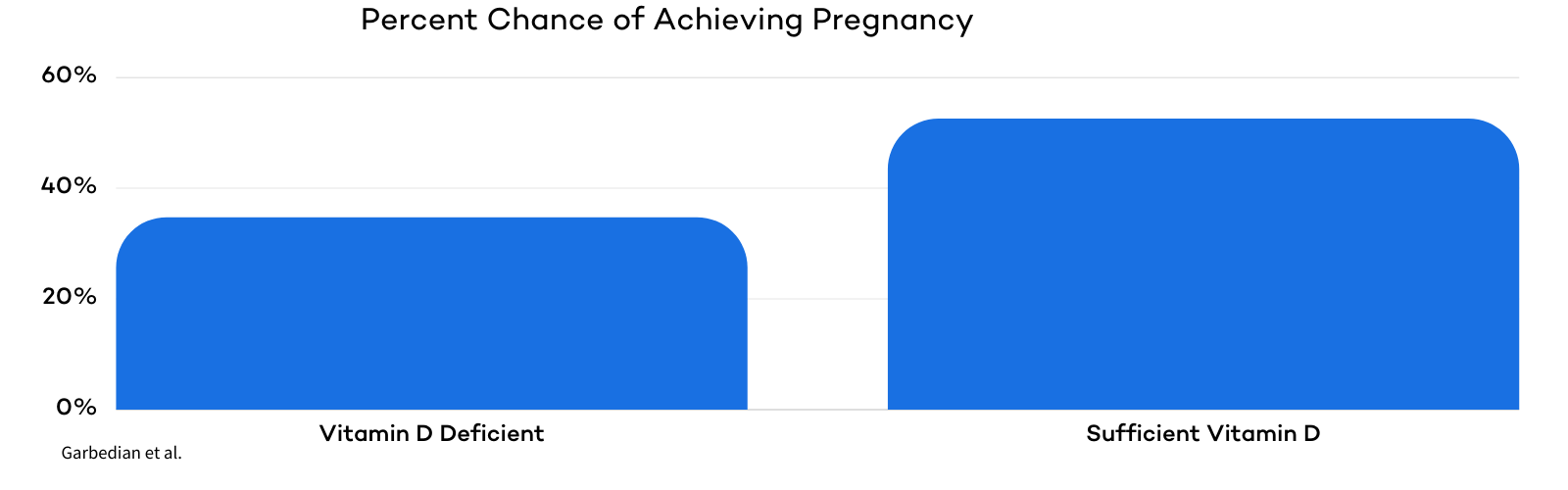
Others
In addition to the three mentioned above specific to getting pregnant with PCOS, there are several more vitamins and nutrients that are known to support overall fertility health.
Click here to read all about the 10 best supplements for PCOS patients!
Medications Used to Treat Infertility For PCOS Patients
Fertility medications are commonly used in fertility treatment, especially for PCOS patients. Medications, along with lifestyle changes, can help PCOS patients to reduce symptoms, ovulate more regularly, and achieve pregnancy!
Metformin
Metformin was originally used solely to manage symptoms of type 2 diabetes. As previously discussed, a large percentage of PCOS patients have insulin resistance and are at risk of developing diabetes. Over the last 20 years, metformin has become one of the most heavily researched and established medications used to help regulate and lower insulin levels and balance the metabolic system of PCOS patients. Research has shown that metformin can also help to induce ovulation in PCOS patients. In one particular study, researchers reported that PCOS patients’ menstrual regularity improved significantly and their androgen levels were reduced when they were treated with metformin .
Other studies have focused on the combination of metformin along with lifestyle changes to induce ovulation in PCOS patients. These included seven studies on the effects of metformin treatment versus placebo and their effects on PCOS patients. Of the 156 PCOS patients in the studies who received metformin, 72 (46%) ovulated. 154 PCOS patients did not receive metformin treatment and only 37 (24%) ovulated .
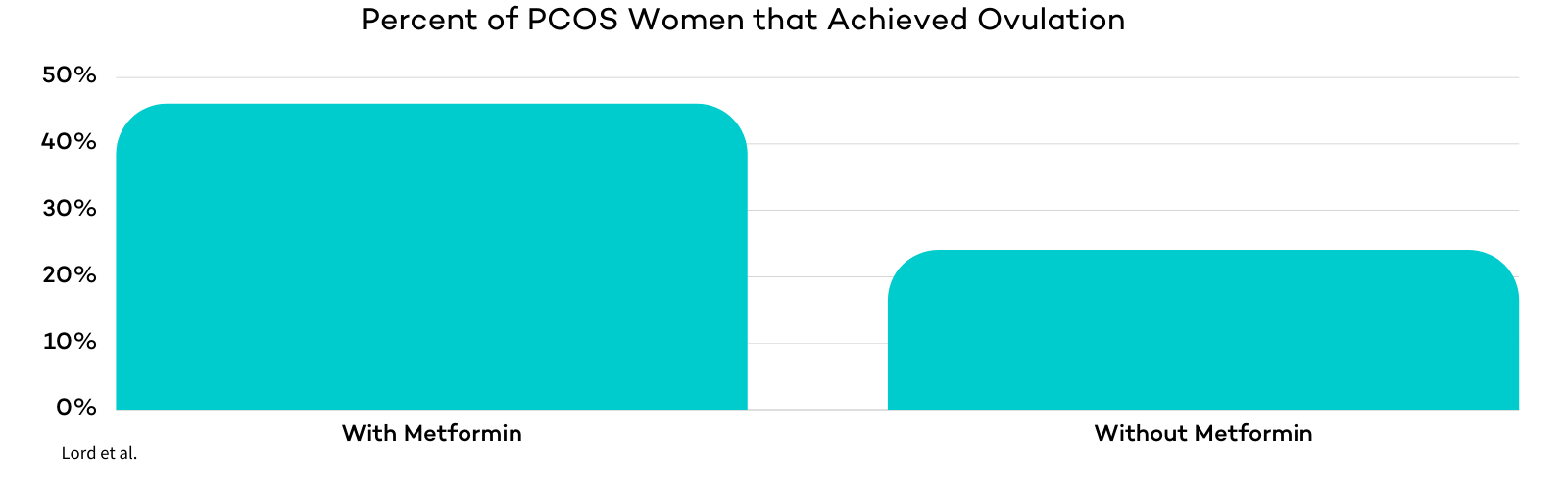
Metformin can also be used by PCOS patients undergoing IVF treatment to reduce the chances of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome . Some fertility specialists believe that metformin may be a suitable alternative to oral contraceptives to treat symptoms caused by hyperandrogenism in PCOS patients. Metformin may help to treat acne and excessive hair growth caused by excess levels of androgens.
Clomiphene (Clomid) & Letrozole
Letrozole is an aromatase inhibitor (lowers estrogen production) that can be used to induce ovulation in patients with irregular ovulation patterns or those who suffer from anovulation. Letrozole improves ovulation by blocking estrogen production, which causes additional follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to be released. The impact of letrozole on fertility has been widely studied. Recently, researchers have focused on letrozole’s ability to treat infertility in PCOS patients.
Clomiphene is categorized as an ovulatory stimulant and is better known by its brand name, Clomid. Clomid is a common oral medication used to treat infertility. It can also be used to induce ovulation in women who do not produce eggs, but wish to become pregnant (like those with PCOS). Clomid is an estrogen receptor modulator that stimulates the production of FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH).
Research on both letrozole and clomiphene to treat infertility in PCOS patients is extensive. Studies have shown that both medications can increase ovulation regularity and the chances of achieving pregnancy for women with PCOS. Recent research however has found that letrozole is more effective than clomiphene for helping women with PCOS to achieve pregnancy. A study conducted by the National Institute of Health (NIH) found that PCOS patients treated with letrozole were more likely to ovulate and to have a live birth compared to women treated with clomiphene. In the study, 374 women were treated with letrozole and 103 (27.5%) of these women had a live birth. 376 women were treated with clomiphene, but only 72 (19.1%) of these women had a live birth . The ovulation rate was also significantly higher for the letrozole group compared to the clomiphene group.
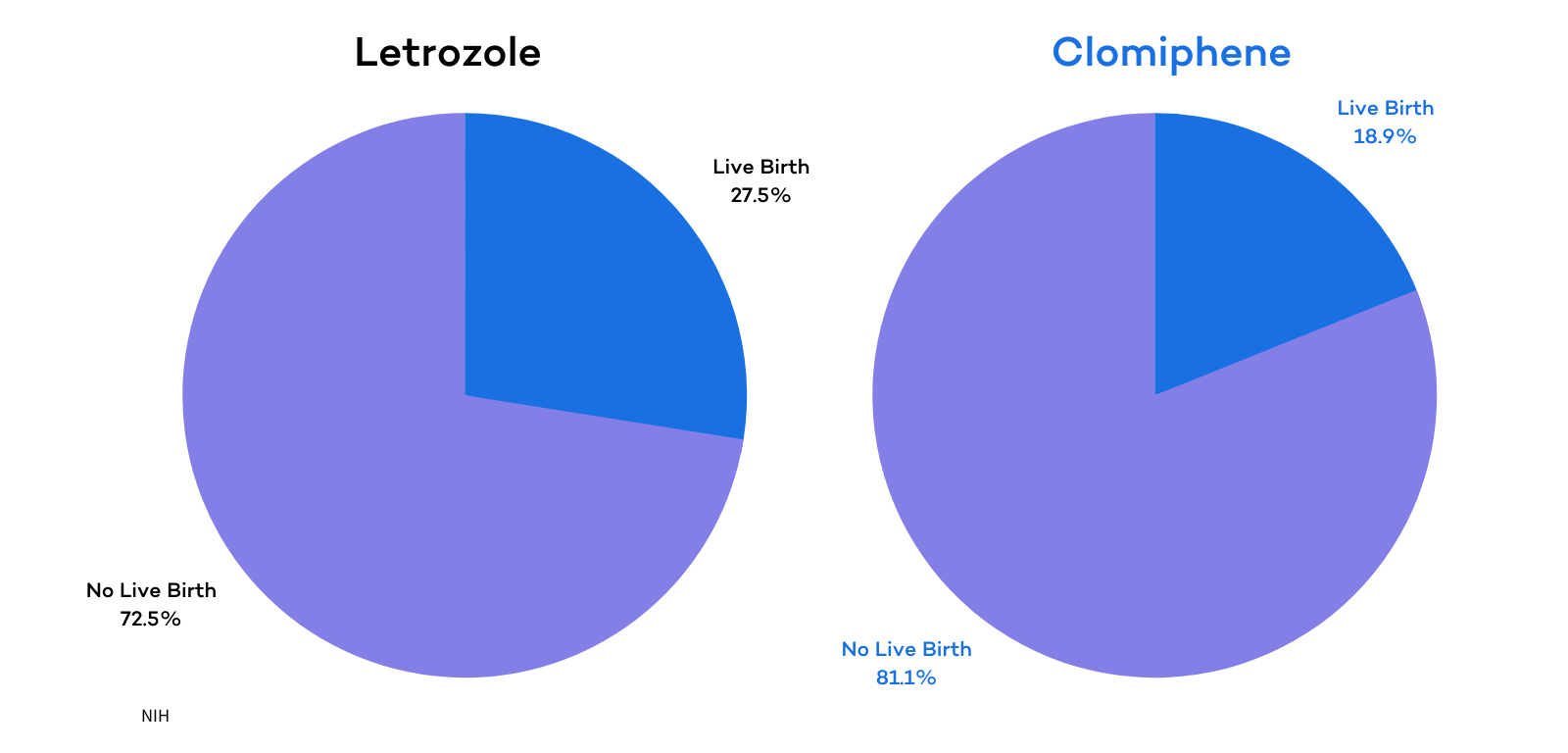
Gonadotropins
Gonadotropins are hormones that impact the ovaries and increase the production of sex hormones. Gonadotropin treatment is usually the second line of infertility treatment for PCOS patients if Clomid or letrozole fail to result in pregnancy. Gonadotropin treatments are administered through injections, so they are often referred to as injectables. Injectable gonadotropins enable over 90% of women with both infertility and PCOS to develop mature follicles and ovulate. Gonadotropin treatment, along with timed intercourse, is associated with an ovulation rate of 70% and a clinical pregnancy rate of 20% per cycle .
Although gonadotropins can increase success rates of natural conception, they are more commonly used with more advanced treatments like intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in-vitro fertilization (IVF). Gonadotropins increase the chances of success with IUI and IVF . The American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) has published research that affirms these conclusions and has shown that gonadotropin treatment is highly efficient to increase ovulation and pregnancy rates in PCOS patients
Click here for more information about using gonadotropins to treat infertility!
Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling (LOD)
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling is a recommended treatment for PCOS patients who are resistant to medications to induce ovulation like clomiphene or letrozole. Ovarian drilling can help these women to ovulate, increasing their chances of achieving pregnancy . Ovarian drilling is a surgical technique that involves the use of a laser or needle to puncture the membranes surrounding the ovary. The reduction of this testosterone-producing tissue leads to reduced testosterone levels in the body. This can assist the ovaries to release an egg each month encouraging regular monthly menstrual cycles. About 50% of women get pregnant in their first year after ovarian drilling surgery .
Ovarian drilling is a one-time treatment, unlike most other PCOS remedies that involve taking medications every month. Ovarian drilling reduces the chances of multiple pregnancies compared to using fertility drugs. Ovarian drilling does not cause ovulation or regular periods in all PCOS patients, but it can help nearly all women respond more to fertility drugs.
Getting Pregnant With PCOS Using Medications & Intercourse
Ovulation induction is usually the first medical treatment that a patient with PCOS seeking infertility treatment encounters. Ovulation induction involves the use of medication (like Clomid/letrozole or a trigger shot) to stimulate ovulation. Ovulation induction using clomiphene or gonadotropins is effective and causes cumulative live birth rates of about 70% . If medications are successful in inducing ovulation, then fertility specialists may recommend starting a timed intercourse cycle. Using gonadotropins with timed intercourse is associated with close to a 70% ovulation rate, a 20% clinical pregnancy rate per cycle, and a 5.7% live birth rate . Gonadotropin treatment is expensive, so it si not common with timed intercourse. Gonadotropins are most commonly used with IUI or IVF because they are associated with higher pregnancy rates for PCOS patients .
For older patients or couples who have been struggling with infertility for a longer period of time, your doctor may skip timed intercourse and recommend either IUI or IVF. Same-sex female couples or women looking to get pregnant on their own with the use of a sperm donor will skip straight to IUI or IVF.
Click here to learn more about ovulation induction!
Getting Pregnant With PCOS Using Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
An IUI, commonly referred to as artificial insemination, is a simple procedure in which sperm is collected, concentrated, and deposited into a woman’s uterus. PCOS patients undergoing intrauterine insemination (IUI) treatment will either use oral medications or injectables to stimulate ovulation. Studies have shown that injectable gonadotropins and IUI increase the chances of successful pregnancy compared to timed intercourse in patients with PCOS . Other studies have found that clomiphene, letrozole, and gonadotropins were equally safe and effective in treating infertility for women with PCOS undergoing IUI treatment .
Click here to learn more about IUI!
PCOS and In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is the most effective fertility treatment available for PCOS patients. IVF treatment offers the highest success rates and quickest time to pregnancy of any Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART). Research has shown that clinical pregnancy and live birth rates are similar for PCOS patients and women who ovulate normally without PCOS . Fertility specialists recommend IVF treatment to patients who have tubal blockages or severe male factors during their initial assessment, are of advanced age, or have failed other lesser treatments. IVF can also be used for patients who have undergone tubal ligation surgery.
IVF involves a multi-week/month process in which eggs are removed from a female’s ovaries, fertilized with sperm in a petri dish, grown inside a lab for several days (usually 3-5), then transferred into the female’s uterus to develop for the remainder of gestation. IVF is used in conjunction with a multitude of medication protocols for PCOS patients to induce ovulation and produce more and higher quality eggs, embryos, and a receptive uterine lining.
Click here to learn more about IVF!
The Bottom Line
A PCOS diagnosis is not the end of the world! It is the most common cause of infertility, and it affects 1 in 10 women of childbearing age. At CNY Fertility, we work to offer our patients with as many resources as possible. Check out the video tab on our Facebook Page to learn from our doctors. You will find videos about improving fertility, managing stress, way more, and specific videos about PCOS.
Click here to watch our doctor from CNY Colorado, Dr. Magarelli, discuss all things PCOS!


