Hydrosalpinx Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and IVF Success Rates
Quick Facts — Hydrosalpinx at a Glance
- What it is: A condition in which the end portion of one or both fallopian tubes becomes fluid-filled and swollen, blocking egg pickup and transport
- Where it occurs: Most commonly at the fimbrial end of the tube near the ovary, preventing the ovulated egg from entering the tube
- Common cause of infertility: Tubal factor infertility accounts for about 25–35 percent of female infertility
- Diagnosis tools: Hysterosalpingogram (HSG), transvaginal ultrasound, laparoscopy
- Best treatment before IVF: Salpingectomy or proximal tubal occlusion
- IVF impact: Untreated hydrosalpinx reduces implantation rates by about 50 percent and increases miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy risk
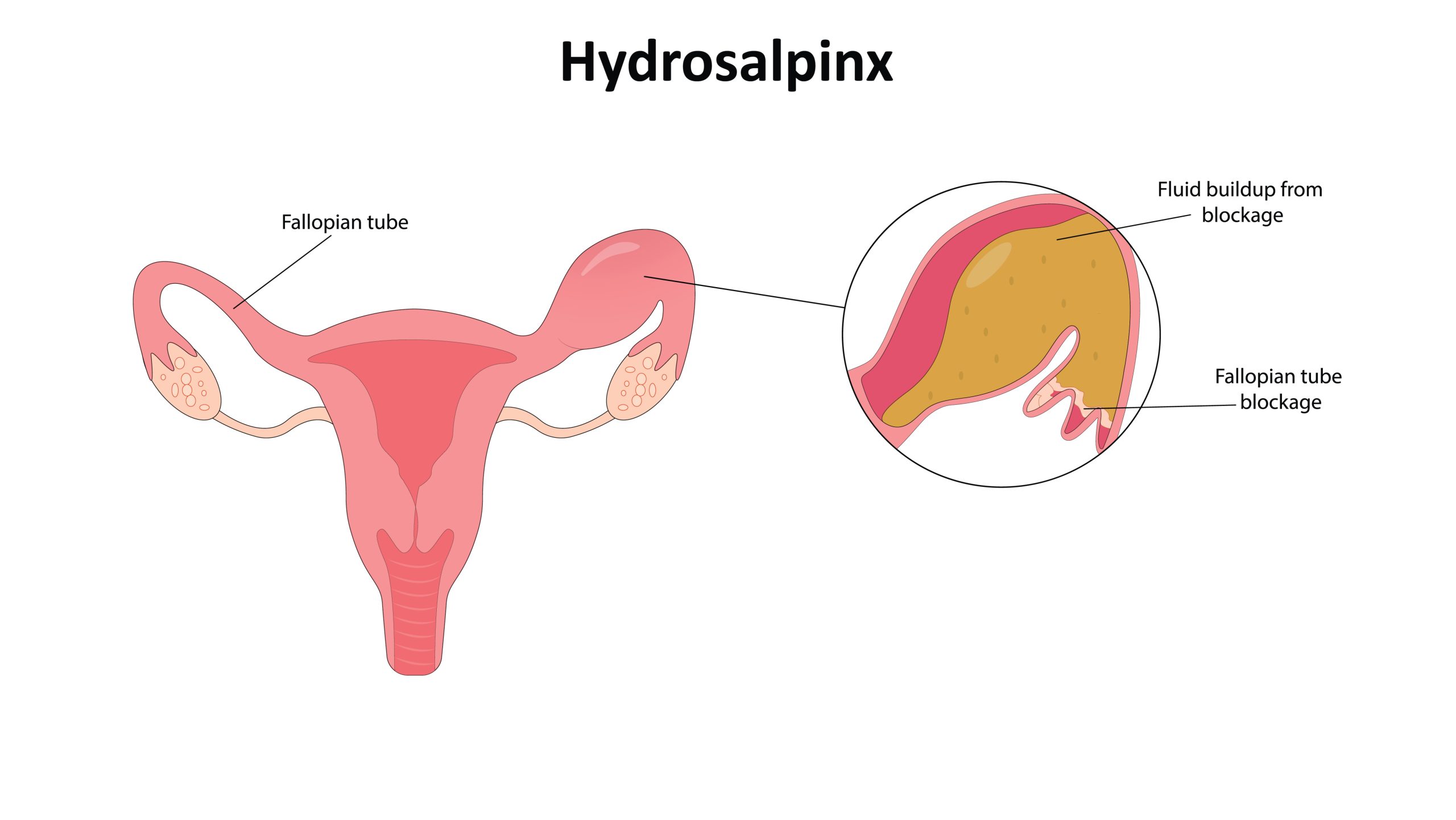
Hydrosalpinx is a form of tubal factor infertility in which fluid becomes trapped inside a fallopian tube after infection, inflammation, or surgery damages the delicate inner lining of the tube. The word hydrosalpinx comes from Greek, where hydro means water and salpinx means tube.
Most cases occur at the fimbrial end of the tube, which is the finger-like portion near the ovary responsible for capturing the egg at ovulation. When this end becomes scarred and sealed, fluid accumulates inside the tube and the egg can no longer enter.
What Is Hydrosalpinx?
Hydrosalpinx occurs when infection, inflammation, or physical injury damages the fallopian tube lining. Scar tissue seals the end of the tube, trapping inflammatory fluid inside.
The condition may affect one tube or both. Bilateral hydrosalpinx results in complete infertility without assisted reproduction.
Even if fertilization were to occur, the swollen tube often blocks the embryo from traveling to the uterus, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy, a life-threatening condition in which the embryo implants inside the tube.
What Causes Hydrosalpinx?
The most common causes include
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- untreated sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia or gonorrhea
- endometriosis
- prior abdominal or pelvic surgery
- ruptured appendix
- adhesions
- pelvic trauma
- congenital tubal abnormalities
- some pelvic tumors
Hydrosalpinx Symptoms
Many patients have no noticeable symptoms. When symptoms occur, they may include :
- pelvic or lower abdominal pain
- abnormal vaginal discharge
- discomfort during intercourse
- difficulty getting pregnant
- In some cases, ectopic pregnancy
Hydrosalpinx does not directly cause weight gain, although bloating or pelvic pressure may create a sensation of fullness.
Can Hydrosalpinx Burst?
True rupture is rare. However, severely distended tubes may leak toxic, inflammatory fluid back into the uterus. This fluid is harmful to embryos and significantly reduces implantation rates.
Can Hydrosalpinx Go Away on Its Own?
Hydrosalpinx does not resolve spontaneously. Antibiotics may treat infection, but cannot reopen a scarred fallopian tube. Once closed, the tube remains blocked unless surgically treated.
How Is Hydrosalpinx Diagnosed?
The most common diagnostic test is a hysterosalpingogram, where dye is injected through the cervix into the uterus and fallopian tubes. If the dye does not spill freely, hydrosalpinx is suspected.
A transvaginal ultrasound may reveal a dilated, fluid-filled tube, but it often misses milder cases.
Laparoscopy allows direct visualization of the fallopian tubes and is considered the gold standard diagnostic method.
Hydrosalpinx Treatment Options
Salpingectomy
Complete surgical removal of the affected tube. This is the most effective treatment prior to IVF and eliminates toxic fluid exposure.
Salpingostomy
A minimally invasive procedure that attempts to reopen the sealed end of the tube. This can restore natural fertility in select cases but carries a higher recurrence risk.
Proximal tubal occlusion
The tube is clipped or cauterized near the uterus to prevent toxic fluid from leaking backward.
Sclerotherapy
Ultrasound-guided drainage with chemical collapse of the tube. Long-term success data is limited.
Hydrosalpinx and IVF Success
Hydrosalpinx decreases IVF implantation rates by approximately 50 percent and increases miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy risk because inflammatory fluid refluxes into the uterus and interferes with embryo development and endometrial receptivity.
Removal or occlusion of the affected tube prior to IVF restores pregnancy rates to levels comparable to women without tubal disease.
Hydrosalpinx Fertility Outlook
With proper surgical management, IVF success rates in patients with hydrosalpinx become similar to those without tubal disease. Early diagnosis and treatment preserve fertility potential and dramatically improve outcomes.
FAQ
Does hydrosalpinx always cause infertility?
Often yes when both tubes are affected. Even unilateral disease reduces fertility and IVF success.
Is surgery always needed before IVF?
Most specialists strongly recommend tube removal or occlusion prior to IVF to improve implantation and live birth rates.
Can hydrosalpinx cause ectopic pregnancy?
Yes. A blocked tube increases the risk of dangerous ectopic implantation.
Will repairing the tube restore fertility?
Tubal repair may work in select cases, but IVF after salpingectomy consistently yields the best results.
Hydrosalpinx: The Bottom Line
Hydrosalpinx is a serious but highly treatable cause of infertility. Treating the condition before IVF dramatically improves pregnancy outcomes and protects long-term fertility potential.

