How to Improve Egg Quality after 40: Lifestyle Tips and Supplements
We discuss various nutrients and dietary supplements in this article that may or may not be helpful. If you purchase recommended products, services, or treatments, it may benefit CNY Fertility financially. Read more about our financial relationships here. The supplements discussed in this article are not intended to treat, cure, or prevent any disease. If you are pregnant, take any medications, or have been diagnosed with a medical condition, consult with a healthcare provider before taking any dietary supplement.

If you’ve come to this article looking for ways to improve egg quality after 40, you’re likely already aware that fertility naturally declines with age.
As women get older, both the number of available eggs and the proportion of genetically normal eggs decrease, making conception more difficult and increasing the risk of miscarriage.
While it’s not possible to stop the natural decline in egg quality that occurs with aging, research suggests that certain lifestyle changes, dietary patterns, and targeted fertility supplements may help support egg quality and the ovarian environment during the final stages of egg development. For some women, these strategies may help optimize fertility potential and improve the chances of pregnancy.
In this article, we’ll explore what egg quality means, how age affects it, and practical steps women over 40 can take to support egg health, including nutrition, lifestyle factors, and evidence-based supplements.
What Is Egg Quality After 40?
Egg quality refers to an egg’s ability to develop into a healthy embryo and result in a successful pregnancy.
After age 40, egg quality declines primarily because a higher proportion of eggs contain chromosomal abnormalities (aneuploidy), which reduces implantation rates and increases miscarriage risk.
Fast Facts
- Egg quality declines with age due to increasing chromosomal abnormalities
- Most eggs in women over 40 are chromosomally abnormal
- Poor egg quality is a leading cause of infertility and miscarriage after 40
- Egg development occurs over approximately 90 days
- Lifestyle and nutritional factors may support egg development, but cannot reverse chromosomal aging
Why Does Egg Quality Decline With Age?
Egg quality declines with age primarily because the biological processes that ensure proper chromosome separation during meiosis become less reliable over time. When this process breaks down, eggs are more likely to contain missing or extra chromosomes, a condition known as aneuploidy.
Females are born with all of the eggs they will ever have, stored in the ovaries in an immature, developmentally arrested state. These eggs can remain dormant for decades before being recruited to resume maturation.
After puberty, a small group of eggs is continuously recruited from this resting pool to enter the final stages of development. Only one egg typically reaches full maturity and is ovulated each cycle, while the remaining eggs naturally degenerate.
Maturing an egg into one capable of fertilization is a complex and energy-intensive process. Human IVF research suggests that oocyte developmental competence is closely linked to cellular energy availability and mitochondrial function.
In addition, studies using ultrasound Doppler during IVF cycles have found that follicular blood-flow measurements are associated with oocyte recovery and early embryo quality, highlighting the importance of oxygen and nutrient delivery within the follicular environment.
As women age, the ovaries become less efficient at meeting these demands. This increases the likelihood that developing eggs accumulate genetic errors, which is why eggs from women over 40 are significantly more likely to be chromosomally abnormal.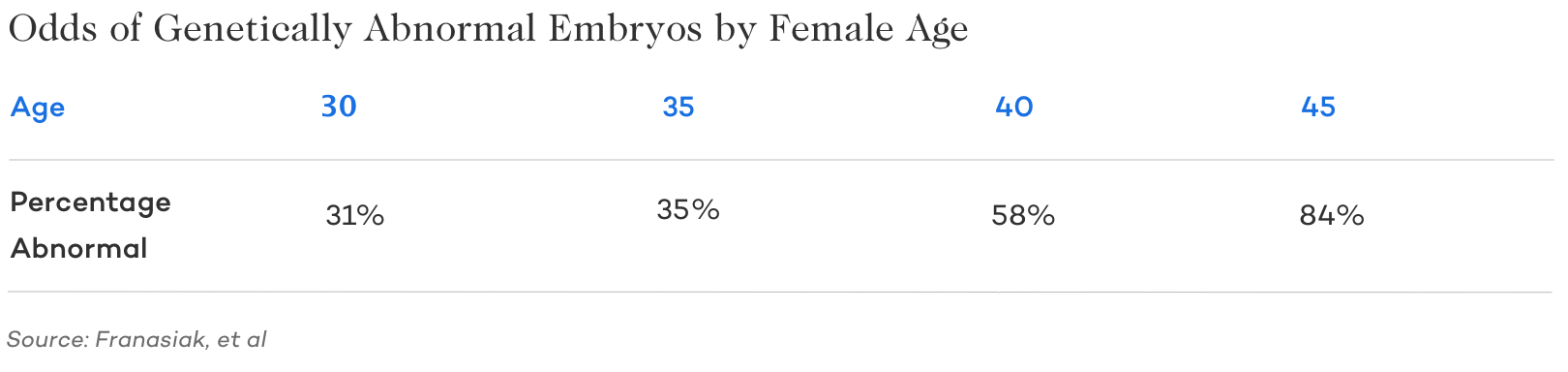
How Is Egg Quality Assessed?
Egg quality can be evaluated in several ways, but most reproductive endocrinologists agree that chromosomal integrity is the most important factor. In practical terms, this refers to whether an egg contains the correct number of chromosomes required for normal embryo development.
As maternal age increases, the proportion of eggs with chromosomal abnormalities rises significantly.
These age-related genetic changes are a primary reason fertility declines over time and why the risks of implantation failure and miscarriage increase after age 40.
How Long Does It Take to Improve Egg Quality?
The final stages of egg development take approximately 90 days, from initial recruitment to ovulation.
For this reason, fertility specialists often recommend beginning supportive interventions—such as targeted supplements, acupuncture, and dietary or lifestyle changes—three to four months before trying to conceive or starting fertility treatment.
That said, it’s important not to feel discouraged if you’re working within a shorter timeframe. Even making supportive changes for a few weeks may help improve the ovarian environment during this critical window and is still worthwhile.
What Foods and Diets Improve Egg Quality After 40?
Diet and nutrition play a critical role in overall health, including reproductive health. When trying to conceive, specific dietary patterns and nutrients may help support ovarian function and egg development.
Some foods commonly recommended for fertility support include liver, fish, and full-fat dairy products, which are natural sources of vitamin A. Adequate vitamin A levels are important for normal oocyte maturation, ovarian response, and early embryonic development.
Research also suggests that diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids found in foods such as fatty fish, oysters, and flax seeds may help support reproductive function and egg quality. Omega-3s play a role in cell membrane integrity, inflammation regulation, and ovarian health, all of which are relevant to egg development.
The Fertility Diet
At CNY Fertility, we recommend eating a diet high in fat and low in carbohydrates. A high-fat, low-carb diet helps to improve overall fertility and egg quality in two main ways:
Reducing inflammation
Balancing reproductive hormones
Inflammation can cause tissue damage and reduce blood flow to the ovaries. This impairs nutrient delivery and egg development. Proper nutrition and blood flow are essential to ensure that eggs develop normally and result in high-quality oocytes.
To reduce inflammation and balance hormones, we recommend increasing dietary fat intake and reducing carbohydrates. Fat supports cell structure, hormone production, nutrient absorption, and energy availability. Eggs, like all cells, rely on these processes for proper development.
When you consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which raises blood sugar, increases inflammation, and dysregulates reproductive hormones.
For full information on the benefits of eating a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet, see Dr. Kiltz’s Keto Cure.
Avoid Caffeine and Alcohol
Excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption have been associated with impaired female fertility.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Egg Quality After 40
Sleep
Quality sleep supports hormone regulation, cellular repair, and reproductive health. Melatonin also acts as an antioxidant within the ovary and may help protect oocytes from oxidative stress.
Avoid Smoking
Cigarette smoking increases oxidative stress and DNA damage within egg cells, contributing to earlier ovarian aging and reduced egg quality.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can disrupt ovulation and reproductive hormone signaling and may negatively affect egg development.
Get Moderate Physical Activity
Moderate physical activity, including walking, stretching, and yoga, has been associated with improved overall reproductive health and stress regulation.
Adequate ovarian and follicular blood flow supports the delivery of oxygen and nutrients needed for egg development. Extremely intense or excessive exercise, however, may negatively affect fertility and should be avoided when trying to conceive.
Supplements to Improve Egg Quality After 40
Fertility supplements may help support egg quality in women over 40 by supporting mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress, and promoting a healthier ovarian environment during egg development.
Fish Oil (Omega-3s)
Omega-3 fatty acids support cell membranes, inflammation regulation, and hormone signaling and may help support ovarian function and egg quality.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
CoQ10 supports mitochondrial energy production within egg cells. Research suggests it may improve markers of egg quality and ovarian response, though it cannot reverse age-related chromosomal abnormalities.
Vitamin A, Vitamin E, Zinc, Folate
These nutrients play supportive roles in oocyte maturation, antioxidant defense, and cell division and may contribute to overall reproductive health when used appropriately.
Fertility Supplements We Commonly Recommend
At CNY Fertility, we often recommend comprehensive fertility supplement combinations that include many of the nutrients discussed above. These formulations are designed to support egg quality, hormonal balance, and overall reproductive health in women over 40.
Because individual needs vary, supplement recommendations should always be personalized and used alongside appropriate medical care, nutrition, and lifestyle support.
Many of our clients use a combination of Molecular Fertility’s Peak Prenatal, Ovarian Bloom, VIVOMEGA Fish Oil, and Immunoglobulin.
How to Improve Egg Quality After 40: The Bottom Line
Egg quality naturally declines with age, largely due to increasing chromosomal abnormalities. While no supplement or lifestyle change can reverse this process or restore egg quantity, many women over 40 can still benefit from supporting the ovarian environment during the final stages of egg development
Prioritizing sleep, stress regulation, moderate physical activity, nutrient-dense nutrition, and evidence-based supplements may help support reproductive health and fertility potential. If you are over 40 and trying to conceive, working with a fertility team can help you determine the most appropriate options based on your goals and timeline.




