How to Increase Sperm Count, Motility, Morphology And Overall Male Fertility
Although it may come as a surprise, up to half of all infertility cases are linked in part or entirely to male factor infertility. The encouraging news is that men continually produce new sperm, and with the right lifestyle changes, it is possible to significantly improve sperm count, motility, morphology, and overall fertility potential.
Pro Tip: Sperm take approximately 40 to 80 days to develop from start to finish. This means that making positive changes at least 40–90 days before a semen analysis, attempting conception, or starting fertility treatments like IUI or IVF can maximize the benefits for sperm health.
Assessing Male Fertility
Before exploring how to improve male fertility, it is helpful to understand how it is evaluated.
The process usually begins with a semen analysis, which evaluates key parameters such as sperm count, motility, morphology, and overall semen quality.
Of course, the very first sign may simply be recognizing that you and your partner are having difficulty conceiving, which then leads to testing and further evaluation.
The semen analysis is the gold standard for evaluating sperm health and male fertility. This simple test provides a detailed look at sperm count, motility, and overall viability, helping doctors determine whether low sperm count or sperm dysfunction may be contributing to infertility.
While a semen analysis collects a variety of data points, it primarily focuses on three key attributes of sperm:
- Sperm Count: the concentration of sperm per mL of semen
- Sperm Motility: how well sperm move with forward progression
- Sperm Morphology: the shape and appearance of sperm
If a semen analysis returns abnormal results, your fertility specialist may recommend further testing to better understand the underlying issues.
It is important to remember that a semen analysis only reflects your sperm health at one specific moment in time. There are many effective ways to increase sperm count and improve overall fertility, which is exactly what the rest of this article will explore.
How to Increase Sperm Count, Motility, and Overall Male Fertility Naturally
While you may have come to this article searching for foods, supplements, or lifestyle changes that can boost sperm count and motility, it is equally important to recognize that removing certain habits or exposures can be just as powerful as adding new ones.
In this section, we’ll break down both what to avoid and what to incorporate to support better sperm count, motility, and overall male fertility.
Quit Smoking
The evidence is clear: smoking is detrimental to nearly every measure of male fertility. One extensive study involving more than 2,000 men found that heavy smokers had 19% fewer sperm compared to nonsmokers.
Another study of more than 1,700 men confirmed the same conclusion; smoking significantly reduces semen quality and negatively impacts male fertility.
| Sperm Density | Sperm Count | Sperm Motility |
| -15.3% | -17.5% | -16.6% |
The evidence does not stop there. A host of other studies show that smoking has a consistently negative effect on male fertility.
Interestingly, researchers have also identified potential mechanisms by which tobacco damages fertility. Zinc, a critical nutrient for sperm production, appears to be reduced in semen due to smoking. One study found that seminal zinc levels were closely linked to the extent of sperm damage, with smokers who maintained normal zinc levels showing less impairment.
Still, the risk remains significant. Additional research on oral tobacco and nicotine metabolites in semen shows that toxins in tobacco smoke are the true culprits behind the damage.
The Takeaway on Smoking
Quitting smoking can improve sperm count, motility, and overall male fertility.Limit Alcohol
In the past, most research on alcohol and fertility focused on women, largely due to the well-known risks of drinking during pregnancy. However, more recent studies have turned their attention to men, and the findings are clear: alcohol can negatively impact male sexual health and fertility.
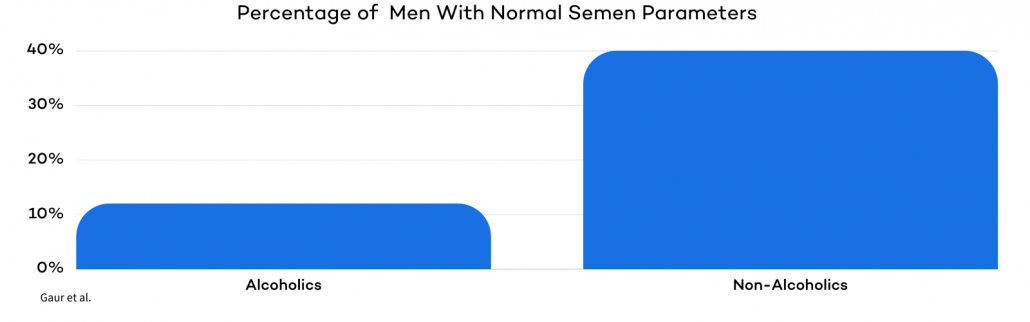
One study compared sperm quality between alcoholic and non-alcoholic men and found a progressive decline in semen quality with increased alcohol consumption.
Sperm volume, vitality, and survival rate all decreased as alcohol intake rose. Among alcoholic men, only 12% had normal semen parameters, compared with 37% of non-alcoholic men. The researchers concluded that alcohol abuse directly impairs sperm production and morphology.
Another study focused particularly on men with a history of chronic alcohol intoxication. The study showed a dramatic improvement of semen quality within three months of alcohol withdrawal. .
A review of 15 studies on alcohol and male fertility found that daily alcohol consumption consistently reduces sperm morphology and semen volume.
In addition, combining alcohol and tobacco use has been tied to declining semen quality and increased sperm DNA damage.
The Takeaway on Drinking
Heavy drinking negatively impacts sperm health. Alcohol consumption can shrink the testes, alter sperm shape, size, and movement, and lower testosterone levels.
The encouraging news is that these effects appear to be reversible! Since sperm take about 70 to 80 days to fully develop, men who want to conceive should consider reducing alcohol intake at least three months before trying for a pregnancy.
Get Tested for STIs and STDs
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are known to negatively affect male reproductive health.
Studies show that chlamydia can cause inflammation in the testicles, which may lead to epididymal obstruction, a condition that blocks the pathway connecting the testicle to the reproductive system. In addition to male fertility issues, untreated chlamydia can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women.
STDs are also linked to infectious semen and a higher risk of transmitting the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In addition to immunodeficiency, HIV also leads to semen deterioration in men. If transmitted to the female partner, HIV can reduce pregnancy rates and increase miscarriage risks.
The global burden of STIs is significant. A review published by the World Health Organization estimated that in 2012 alone, there were about 273 million cases of curable STIs among adults aged 15–49, including 128 million cases of chlamydia, 27 million cases of gonorrhea, 101 million cases of trichomoniasis, and 18 million cases of syphilis.
The Takeaway on STIs and STDs
Testing and treating curable STIs can alleviate sperm blockages caused by inflammation and improve both male and female fertility outcomes.Keep Those Swimmers Cool: Avoid Hot Tubs, Saunas, and Other High Heat Situations
Spermatogenesis, the production and development of mature sperm, occurs in the testicles. Testicular temperature is naturally about 30–45°F cooler than the rest of the body, and this cooler environment is necessary for healthy sperm production.
Higher temperatures raise testicular metabolism, leading to sperm damage.
One study found that heat stress reduced motility and increased the percentage of sperm with both major and minor defects.
A study from the University of California, San Francisco, showed that frequent exposure to hot tubs or jacuzzis can contribute to male infertility. Eleven men who regularly used hot tubs were asked to avoid “wet heat” for at least three months. Five participants (45%) saw their total motile sperm counts increase by an average of 491% within three to six months.
Among responders, motility improved from 12% to 34%. Interestingly, five of the six non-responders were chronic tobacco users, suggesting tobacco may worsen heat-related sperm damage.
Another study published in 2013 investigated continuous sauna exposure and found similar outcomes. Sauna heat impaired spermatogenesis, altering sperm parameters and DNA packaging.
The Takeaway on Heat, Saunas, and Jacuzzis
Avoid excessive heat exposure from hot tubs or saunas while trying to conceive. The good news is that the damage heat causes to sperm motility and count appears to be reversible once exposure is stopped.
The Effects of Environmental Toxins on Male Fertility
Exposure to environmental toxins has become more common over the past few decades. Studies suggest this exposure can negatively affect semen quality, including sperm concentration, motility, and morphology.
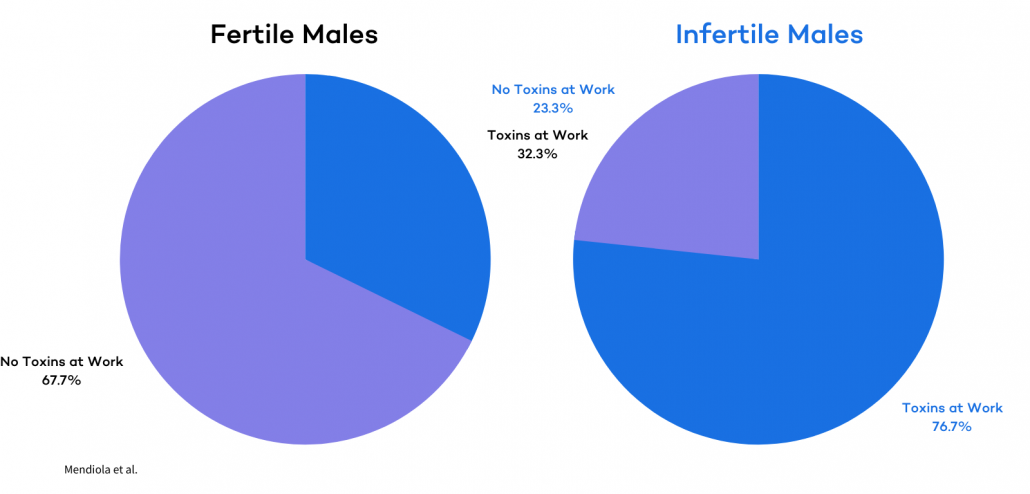
Occupational exposure is one of the most frequent sources of risk. A study in Spain examined men seeking infertility treatment and compared 30 infertile males to 31 men with normal sperm parameters.
Of the infertile group, 23 had been exposed to toxins or pollutants at work, while only 10 of the fertile men had similar exposures.
The toxins included glues, solvents, and silicones. The findings suggest that occupational exposure to environmental toxins may be a direct cause or a significant contributing factor to male infertility.
Cumulative research confirms that environmental toxins reduce fertility and significantly lower the chances of IVF success.
The most disruptive toxins include:
- Organochlorine compounds: Present in chlorinated pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls, and dioxins.
- Bisphenol A (BPA): Often found in polycarbonate plastics like water bottles, food storage containers, and some medical devices. Also present in epoxy resins used to coat the inside of cans, jar lids, and even some water supply pipes.
- Organophosphate pesticides and herbicides: People are exposed to these through agricultural work, dietary residues on food, and contaminated water or soil, with additional risks from inhalation or skin contact during spraying.
Other harmful agents, including heavy metals and air pollutants, have also been linked to reduced fertility. For men, these toxins contribute to infertility by disrupting the endocrine system and damaging the reproductive tract.
Unfortunately, toxins are difficult to avoid altogether, especially for individuals regularly exposed through their work.
One of the most infamous toxins, BPA, is used in plastics and is commonly found in food packaging, canned goods, and water bottles. BPA and many pesticides act as xenoestrogens, chemicals that mimic estrogen. Research has shown that xenoestrogens reduce motile sperm counts and overall semen quality.
The Takeaway on Environmental Toxins
Environmental and occupational toxin exposure can play a major role in reducing male fertility.
The good news is that some exposures can be minimized with simple lifestyle changes. Limiting products known to contain toxins, choosing whole foods over processed, and avoiding non-stick cookware (which contains similar chemicals to pesticides) are straightforward steps to reduce risks.
Tips to Reduce Exposure to Anti-Fertility Factors
Limit Soy Intake
Soy products contain phytoestrogens, which, like xenoestrogens in chemicals and pesticides, are known to damage sperm concentration.
A study of 99 men attending a fertility clinic found that higher soy intake was associated with lower sperm concentration.
The results of this study were also highlighted by Harvard Health Publishing at Harvard Medical School.
While soy is often praised for health benefits like lowering cholesterol and is a staple in many Asian diets, its potential adverse effects on male fertility deserve careful attention.
Don’t Eat Trans Fats
Trans fat can be found in food either as naturally occurring or artificial trans fats.
- Naturally occurring trans fats are produced by animals and can be found in milk and meat products. They are not linked to adverse effects on male fertility, and usually consumed in such small amounts that any effect would be negligible.
- Artificial trans fats are most commonly found in processed foods that contain “partially hydrogenated oils.”
In the past, research focused mainly on how trans fats increase the risk of heart disease. Research has also shown that trans fats are linked to a decrease in sperm counts.
To reduce trans fat intake, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommends limiting foods that contain hydrogenated vegetable oils and checking food package ingredient lists carefully.
Keep in mind that artificial trans fats in processed foods are the fertility concern. Limiting processed foods with “partially hydrogenated oils” is the best way to protect sperm health.
Limit Stress
Stress is how the brain and body respond to pretty much any demand put upon it, either emotionally or environmentally.
Over time, continued stress can cause serious health problems. Stress affects nearly every system in the body, so it is no surprise that it impacts male fertility.
Stress is one of the most complicated causes of male infertility because a diagnosis of infertility often makes the problem worse. Stress can increase after diagnosis, during follow-up appointments, and following failed in vitro fertilization treatments.
Studies have found that semen parameters and stress are linked. Stress can negatively impact luteinizing hormone (LH) and testosterone production, which complicates spermatogenesis and reduces sperm quality.
Infertility-related stress can arise from social pressures, testing, diagnosis, treatment failures, and the costs of fertility care.
Couples undergoing fertility treatment often experience distress, depression, anxiety, and decreased quality of life. Fortunately, relaxation techniques such as yoga, exercise, and meditation can help combat stress related to infertility.
A review of 37 studies found that relaxation techniques reduced negative emotions in patients undergoing medical treatment.
In more severe cases, fertility specialists may recommend psychological intervention. A review of 12 studies found that psychosocial interventions improved psychological outcomes, strengthened marital relationships, and increased pregnancy rates among infertile couples.
Recognizing the importance of stress reduction for better outcomes, we offer emotional fertility support and resources to provide patients with empathy and encouragement.
Occupational stress and its effects on male fertility have also been studied. One study found that stressful situations at work impacted semen volume and the percentage of sperm with normal motility. The results confirmed that workplace stress can have a negative impact on semen quality.
Get Enough Sleep
Sleep is essential for optimal male fertility.
Many studies have confirmed that insufficient sleep can contribute to serious health conditions like obesity, diabetes, and infertility.
One study of 981 healthy men examined the effects of sleep patterns on sperm morphology, count, survival, and motility. Sperm counts and survival rates were significantly lower in men considered “short sleepers” compared to those who got sufficient rest.
Short sleepers, defined as men who sleep fewer than six hours per night, also had reduced semen motility compared to average and long sleepers. The study concluded that both short and longer than average sleep durations, as well as late bedtimes, were associated with impaired sperm health.
In addition to duration, sleep quality also plays a crucial role in male fertility. One study on 970 men undergoing fertility treatment found that poor sleep quality was correlated with lower total motility, progressive motility, concentration, sperm count, and normal morphology.
To increase your fertility, focusing on sleep is crucial. Aim for 7–8 hours of good quality, restful sleep each night. Lifestyle interventions that can help, include:
- Stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or exercise
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule by waking up and going to bed at the same time each day.
- Increasing morning sunlight and evening low-light exposure to regulate your circadian rhythm and reduce the need for naps.
Start Regular Low-Intensity/Impact Exercise
Exercising provides numerous benefits for fertility and overall health. It strengthens the heart, improves circulation, reduces stress, and helps promote better sleep quality. Studies have shown that men who exercise regularly have higher testosterone levels than inactive men.
Benefits of Regular Exercise for Male Fertility
- Improves circulation and cardiovascular health
- Helps reduce stress and promotes better sleep
- Boosts testosterone levels, which supports sperm production
- Associated with better semen parameters and hormone values
If you are experiencing fertility issues and do not exercise regularly, consider adding 30–60 minutes of low-intensity movement into your daily routine. One study placed 41 overweight and obese men into a 12-week lifestyle modification program that required aerobic exercise training. After the program, all participants showed a significant increase in blood testosterone levels.
Risks of Excessive or High-Intensity Exercise
- Can decrease thyroid hormones and testosterone levels
- Linked to altered sperm density, motility, and morphology in endurance-trained men
- Negatively affects semen parameters, especially morphology, as intensity and volume increase
For men who exercise heavily, there is some encouraging news. Supplementing with zinc has been shown to help counteract the decreases in testosterone and sperm health caused by intense exercise.
Eat Plenty of Healthy Fats!
Fat is the foundation of fertility. It provides the building blocks for every cell in the body and plays a central role in synthesizing reproductive hormones. Dietary fat supplies energy, delivers essential fatty acids that the body cannot make on its own, and allows for the absorption of key vitamins such as A, D, and E—all of which are essential for fertility.
Key Benefits of Healthy Fats for Male Fertility
- Support hormone production, including reproductive hormones
- Provide essential fatty acids for sperm health
- Help absorb vitamins A, D, and E, critical for fertility
- Reduce inflammation, which is directly linked to better sperm quality
- Aid brain function and control blood clotting through fatty acids in animal products
The Link Between Fat, Inflammation, and Fertility
- Inflammation is associated with oxidative stress, which can damage sperm DNA and impair function.
- Studies show that many infertile men suffer from acute or chronic inflammation in the genitourinary tract, and this inflammation contributes to oxidative stress.
- Eating sufficient healthy fats helps reduce inflammation, lowering oxidative stress and improving overall sperm health.
Other Health Benefits
- Lubricates the lymphatic system, which filters out harmful pathogens and supports immunity.
- Maintains optimal circulation and immune system function.
Sources of Healthy Fats
- Well-sourced meats and fatty cuts like ribeye steak
- Fish
- Cheese
- Eggs
- Nuts
Pro tip: Reduce intake of trans fats while increasing healthy fats to optimize fertility
Vitamin D: Get Some Sunshine!
The sun is the best natural source of vitamin D. When your skin is exposed to sunlight, your body makes vitamin D from cholesterol.
Vitamin D can also be obtained from foods like cheese, egg yolks, and fatty fish such as salmon, or through supplementation.
Why Vitamin D Matters for Male Fertility
- Vitamin D plays many roles in overall health and is essential for male fertility.
- Research shows vitamin D has a positive effect on sperm motility.
- Additional studies confirm vitamin D also supports overall semen quality.
The Problem of Vitamin D Deficiency
- About 40% of adults in the U.S. are vitamin D deficient.
- Deficiency is linked to reduced fertility in men, including lower sperm motility and fewer motile sperm overall.
- Fertility specialists recommend supplementing vitamin D to improve sperm concentration, morphology, and motility.
Vitamin D and Testosterone
- Men with vitamin D deficiency are more likely to have low testosterone.
- Supplementing vitamin D can increase testosterone levels by 25% within one year.
Vitamin D and Fertility Treatments
Recent studies suggest vitamin D supplementation can improve pregnancy outcomes for couples undergoing fertility treatments.
Take Your Supplements
While many fertility-boosting vitamins and nutrients are naturally found in food, it is nearly impossible to consume adequate amounts of all of them through diet alone.
Male fertility supplements can help fill these gaps, and research strongly supports the importance of specific vitamins and minerals in improving sperm health. If you plan on taking male fertility supplements, make sure they contain the following ingredients:
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
- Elevated blood levels of CoQ10 have been linked to improved male fertility.
- Supplementation has been shown to improve sperm concentration and motility, especially in men suffering from infertility and asthenozoospermia (poor sperm motility).
- Men with oligoasthenoteratozoospermia (low sperm count and quality) experienced significant increases in concentration and motility after CoQ10 treatment.
- Beyond concentration and motility, CoQ10 supplementation has also been linked to improved total sperm count.
Folate (Vitamin B9)
- Folate is essential for spermatogenesis, the development of sperm cells, and plays a critical role in DNA synthesis and replication.
- Because sperm DNA undergoes numerous replications, proper folate levels are needed to ensure genetic stability and reduce mutations.
- Low folate concentrations are associated with increased sperm DNA damage, reduced motility, and lower sperm counts.
Zinc
- Zinc is one of the most important minerals for male fertility, yet deficiencies are common in men who eat little meat, fish, or eggs.
- Low zinc levels are associated with reduced testosterone, poor sperm quality, and higher infertility risk.
- Supplementation has been shown to increase both testosterone levels and sperm count in zinc-deficient men.
- Research also shows that men engaging in high-intensity exercise, which can lower testosterone, benefit significantly from zinc supplementation.
Medications to Increase Sperm Count, Morphology, and Overall Male Fertility
Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid)
Clomid, the brand name for clomiphene citrate (CC), is one of the most widely used off-label medications for male infertility, even though it is not FDA-approved for men. It is often prescribed to improve sperm count, boost testosterone, and enhance overall fertility. A randomized controlled trial of men with idiopathic oligozoospermia showed that the pregnancy rate in the treatment group was nearly three times higher than in the control group, 37% versus 13.3%. The treatment group also experienced significant increases in sperm count and progressive motility.
Clomid works by stimulating the anterior pituitary gland to secrete higher levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones increase testosterone production and support spermatogenesis in men with low testosterone.
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN)
Low dose naltrexone (LDN) is another medication sometimes used to support male fertility due to its anti-inflammatory properties. By reducing inflammation, LDN is believed to improve blood flow and nutrient delivery to developing sperm.
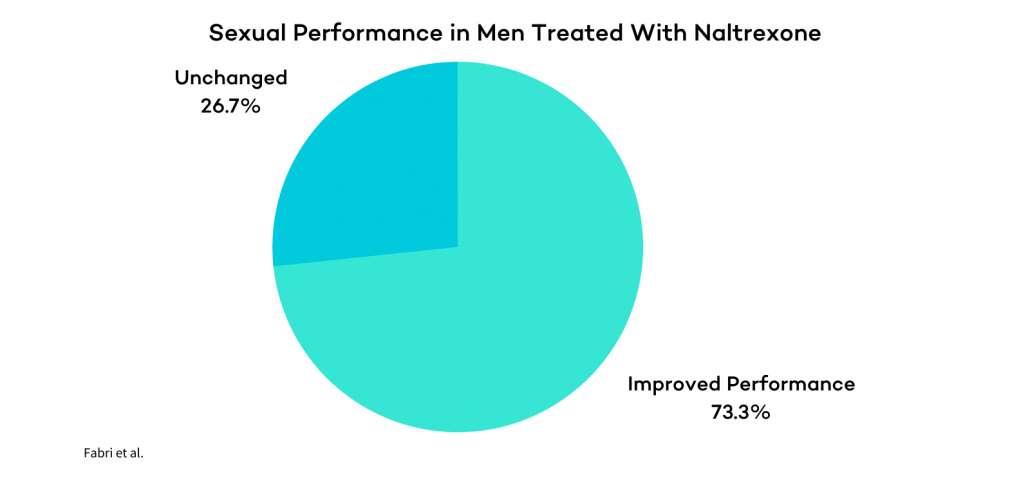
New research also indicates that LDN may be effective for men experiencing erectile dysfunction. In one study of 30 men with idiopathic impotence, 11 out of 15 men treated with naltrexone reported significantly improved sexual performance.
All treated men experienced increases in morning and spontaneous erections, and two months after discontinuing treatment, one-third of participants reported complete recovery of sexual ability.
Human Growth Hormone (HGH)
Research into human growth hormone (HGH) and its role in male fertility is expanding, with evidence showing that HGH plays an important role in spermatogenesis and reproductive function.
Fertility specialists believe HGH may be particularly effective for men who are growth hormone-deficient. One study found that HGH therapy helped restore sperm concentration, morphology, and motility in GH-deficient men.
Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (hCG)
Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), often called the pregnancy hormone, has been FDA-approved to treat certain medical conditions in both men and women.
For men with reduced spermatogenesis caused by inadequate gonadal stimulation, hCG injections can promote testis growth, testosterone production, and sperm development. Research has shown that hCG therapy is effective in inducing spermatogenesis and fertility in gonadotrophin-deficient men.
Another study focused on men with low testosterone who could not produce mature sperm found that hCG treatment could effectively initiate and maintain spermatogenesis.
Additional research has confirmed these results, showing that hCG improves spermatogenesis by raising both intratesticular and serum testosterone levels.
hCG remains the only on-label pharmaceutical therapy specifically approved for the treatment of male infertility. While it is highly effective, hCG therapy is expensive and requires abdominal injections, as it is not available in pill form.
Treatment Options for Improved Pregnancy Rate with Male Infertility
- Interutinary Insemination (IUI) often referred to as artificial insemination, is a simple procedure in which sperm is collected, concentrated, and then deposited directly into the uterus. By bypassing the cervix and bringing sperm closer to the egg, IUI can improve the chances of conception in cases of mild male factor infertility.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is considered the gold standard of fertility care and remains the most effective assisted reproductive technology available. IVF consistently offers the highest success rates and the quickest path to pregnancy, making it a leading option for many couples facing infertility.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): is an advanced laboratory technique used during an IVF cycle. In this procedure, a single sperm is injected directly into a mature egg to create a fertilized embryo. ICSI is especially valuable in cases of severe male factor infertility, where sperm may be unable to fertilize an egg on their own.
- Testicular Extractions: When no sperm is present in the ejaculate, testicular extraction procedures can be performed. These surgical techniques retrieve sperm directly from the male reproductive tract, allowing them to be used in conjunction with IVF and ICSI to achieve fertilization.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: Another emerging option, PRP is a concentrated blood product rich in biomolecules with natural healing and regenerative properties. Testicular PRP is an innovative and experimental approach being explored for men with azoospermia, with the goal of stimulating sperm production so that even a small number of active sperm may appear in the ejaculate for use with IVF and ICSI. At CNY, Dr. Mariabelle Vardiales is currently conducting research on this technique, and while it is still experimental, the early results appear promising.
Increasing Sperm Count, Motility, and Other Male Fertility Parameters: The Bottom Line
Male fertility is highly adaptable: with the right changes, count, motility, morphology, and overall reproductive potential can meaningfully improve.
Because sperm mature over roughly two to three months, consistent habits including better sleep, stress control, smart nutrition, targeted supplements, and avoiding toxins, pay off when sustained for at least 40–90 days.
Start with a semen analysis to get a clear baseline, then pair lifestyle upgrades with evidence-based medical options when needed.
If you’re ready for a tailored plan or want a second look at your results, our team at CNY can help you map the fastest, healthiest path forward.
May your sperm soon be swimming like 2008 Michael Phelps!


